Free consultation with ASO specialists
Doing ASO for the first time or have no idea how to carry out targeted optimization of your app?
We offer one-on-one customized services provided by app marketing specialists
Google Play AI regulations have been implemented, and developers are facing a triple compliance storm
2025-07-25
Platform liability, mandatory disclosure and regional compliance differences are reshaping the game rules of the mobile AI ecosystem.
July 11, Google Play officially put "AI Generated Content Policy"By incorporating core provisions into the Developer Program Policy, it marks the first time that the world's largest app distribution platform has included AI technology in a clear compliance framework. The new regulations require all apps using AI-generated text, images, videos or voice to take responsibility for content and disclose details of technology use in prominent locations."
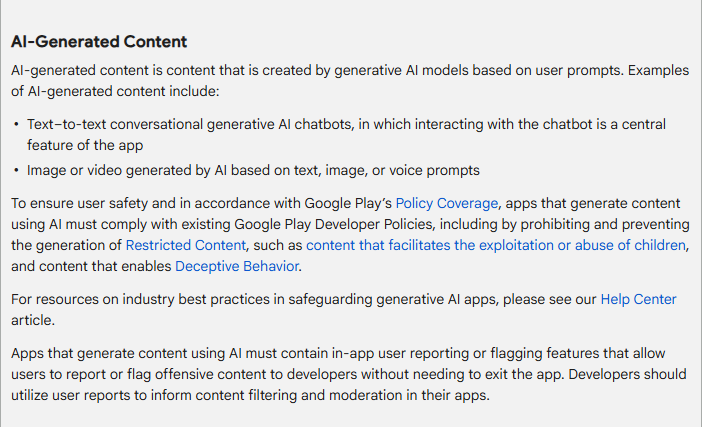
This policy change comes at a critical juncture when AI content is experiencing explosive growth in mobile applications. According to Statista data, global AIGC application downloads are expected to increase by 320% year-on-year in 2025, but the accompanying false information, copyright disputes, and fraud cases have also increased by 280% year-on-year.
An Inevitable Step Under the Wave of Global AI Governance
The policy is not an isolated event, but a microcosm of the tightening global AI regulation.
-
The "Guidelines for Generative AI Responsibility" released by the U.S. FTC at the same time clearly states that even if the AI model is open source, developers are still responsible for the content of downstream applications.
-
This governance model of "risk grading + full-chain accountability" is becoming a global consensus. According to Play Store data, the number of applications removed due to AI content violations in the first half of 2025 increased by 190% year-on-year, with financial, medical, and children's education applications accounting for over 65%.
-
A certain financial application used AI to generate fake user ratings and reviews, which deceived 23,000 users and eventually led to a class-action lawsuit. Such incidents forced Google to shift from "post-event punishment" to "pre-event prevention".
-
Tech giants are vying for the right to govern AI. At its 2025 WWDC conference, Apple released an "AI Application Development White Paper," requiring all applications using Core ML to pass certification from an "Ethics Review Committee." Meta has implemented a "double-blind review" mechanism for AI-generated advertisements.
The EU's AI Act will officially come into effect on August 2, 2025. Generative AI is listed as a "high-risk" category, requiring companies to submit technical documents and undergo third-party audits. Google's move aims to compete for global AI governance leadership through rule-making, paving the way for its Vertex AI developer ecosystem.
The Triple-edged Policy: Responsibility, Disclosure and Transparency of Compliance
-
The absoluteness of responsibility attribution: the collapse of the safe harbor principle
The new policy breaks the traditional "safe harbor principle" applicable boundary. Whether AI-generated content is directly used by developers or generated by users through UGC functions, application owners must bear the main responsibility for content compliance.
If the AI images generated by users through a certain social application involve infringement or violent content, the platform has the right to directly remove the application and hold the developer accountable. This rule completely shifts the pressure of content review from the platform to the developers.
-
The Obligation to Disclose: The Cost of Transparency
The application must clearly indicate the use scenarios of AI technology in the Play Store details page, privacy policy and user agreement. If financial applications use AI to generate investment advice, they must add a warning statement in the function introduction: "This service contains AI analysis and does not constitute professional investment advice."
Google specifically requires that the content disclosed must be "easy to understand", and prohibits the use of vague expressions such as "partially generated by advanced technology". It is recommended to adopt the "black background and yellow text" warning format recommended by the EU's AI Act, so as to meet the three standards of "prominent position + clear language + multi-scene coverage".
-
The Penetration of Compliance Standards: AI is not a Lawless Place
AI-generated content must not circumvent existing policies, including false advertising, pornography and violence, medical fraud, etc. Medical applications that use AI to generate health advice, even if marked "for reference only", still need to comply with medical advertising regulations in various countries, otherwise it may trigger the "unacceptable risk" clause in the EU's "AI Act". The policy clearly states that even if AI-generated content only has a "potential risk" (such as misleading implications), it may still be deemed non-compliant.

Developer Survival Crisis: Five Major Pitfalls and Millions in Fines
-
Financial, medical and educational applications are the first to be affected
If financial applications use AI to generate investment advice, they must submit an algorithm transparency report and third-party audit proof when submitting for review. The review period may be extended from 7 days to 21 days.
-
Significant increase in technical compliance requirements
Developers must provide "digital watermarks" and "training data traceability chains" for AI-generated content. A news application was found to have violated regulations because it could not prove that the AI-generated text did not copy Reuters reports. An image generation application was sued by Adobe for $12 million due to the use of pirated material libraries.
-
Disclosure scene is complicated
In addition to the app store, AI instructions must also be embedded in the startup page, function entry and user agreement. A social application was fined 2.5 million euros by the European Union for only marking the AI image generation function at the end of the privacy policy.
-
User Generated Content (UGC) becomes a high-risk area
If users are allowed to generate AI content, a three-level mechanism of "pre-review + real-time filtering + user reporting" must be established. A writing tool was ordered by the court to pay 5 million US dollars in compensation to the original author for users using AI to generate pirated novels.
-
Regional compliance differences create global challenges
Saudi Arabia requires that all AI-generated content not involve religious elements, while India prohibits the use of AI-generated images of political figures. A game company delayed the launch of its product by 6 months due to its failure to respond promptly to South Korea's new regulations on the appearance of AI-generated characters.
Compliance Survival Guide: From Passive Defense to Active Adaptation
-
Strategic Retreat and Defense in High-Risk Areas
Avoid using AI to automatically generate core content in fields such as medical, financial, and news. A health application limited the AI function to symptom self-check assistance rather than diagnostic advice, successfully passing EU review. For scenarios that must use AI, the "human-machine collaboration" mode can be adopted.
For example, some translation applications require that AI-generated results must be reviewed by professional translators, which improves efficiency and reduces risk.
-
Technology Risk Control and Transparency Disclosure
Adopt the combination of "AI review + manual recheck". A certain e-commerce platform introduced Google Perspective API to filter hate speech, while retaining a 5% manual sampling ratio. Ensure that the training data source is legal and avoid using unauthorized public data.
Refer to the "four-element model" recommended by the EU's AI Act: technology type, usage scenario, data source, and risk warning. An educational application added a note on its details page stating "Some content of this course is generated by AI, with the teacher team supervising throughout," significantly reducing the user complaint rate. If the AI function is upgraded, the disclosure content must be updated synchronously.
-
Global Compliance Architecture
Configure differentiated content strategies for different markets. A social application disabled the AI image generation function in the EU version, while retaining it in the Southeast Asian market but strengthening review. In key markets (such as the EU and South Korea), establish dedicated compliance positions to track policy changes in real time.
It will become a basic requirement for developers to provide "digital watermarks" and "training data traceability chains" for AI-generated content.
Conclusion: Compliance capability becomes a new watershed for AI developers
Google's policy adjustment sends a clear signal: the platform's attitude towards AI has shifted from "encouraging innovation" to "controllable development". As shown by OpenAI's case of regaining market trust through compliance rectification after being fined in Italy, compliance should not be seen as a cost, but should be transformed into brand competitiveness.
Future AI application development will be a comprehensive competition of technical capabilities, legal literacy and global vision. Developers need to establish a full-link content risk control system, including pre-generation review, real-time interception and post-event traceability mechanism, to cope with the content governance challenges in the absolute responsibility era.
The EU AI Act is set to take effect on August 2, and the rapid formation of a global regulatory framework is reshaping the mobile app ecosystem.
Facing a complex policy environment, developers can use AppFast's professional metadata diagnostic tool to quickly identify potential risks on the store page (such as prohibited keywords and mismatched ratings) and generate optimization suggestions. Click Diagnose Now, one-click to improve application compliance and exposure rate, and calmly respond to Google Play policy challenges.
Related recommendations

